Week1 Intorduciton, process, thread
Introduction
An operating system is a program that manages a computer’s hardware
some operating systems are designed to be convenient, others to be efficient, and others to be some combination of the two.
1.1 What Operating Systems Do
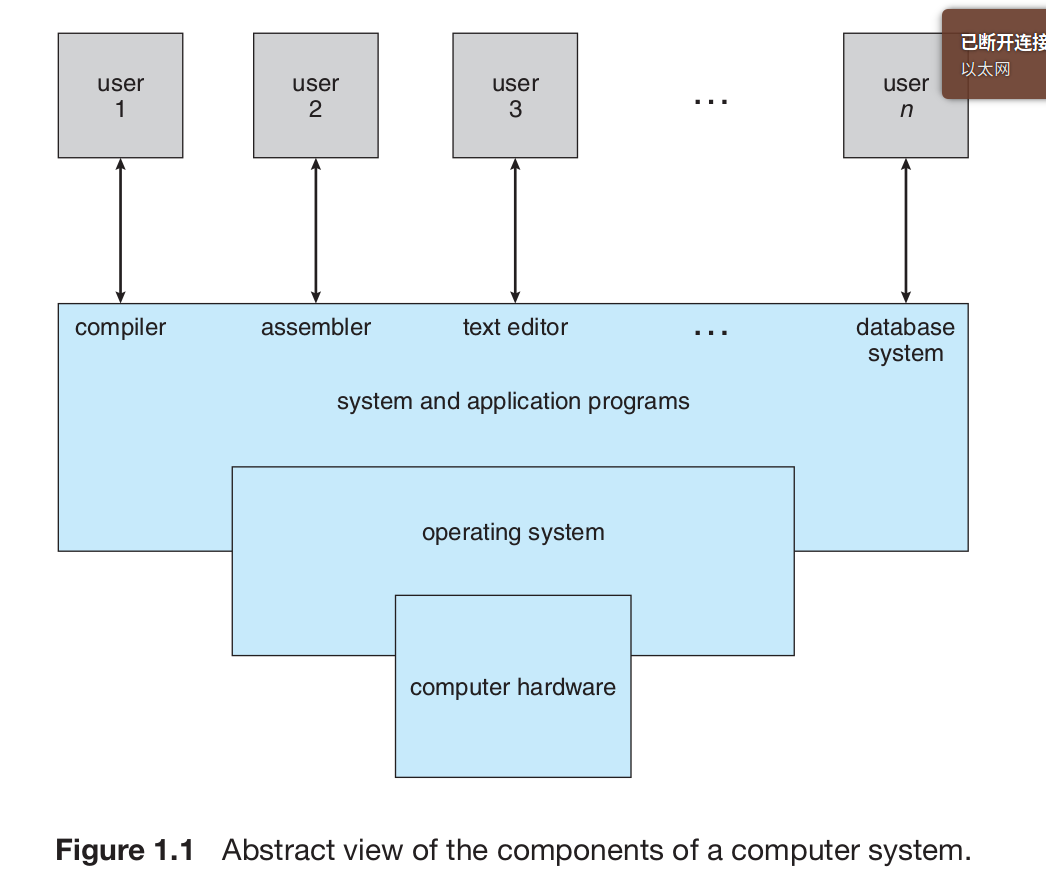
A computer system can be divided roughly into four components: the hardware, the operating system, the application programs, and the users
The hardware—the central processing unit ( CPU ), the memory, and the input/output ( I/O ) devices—provides the basic computing resources for the system. The application programs—such as word processors define the ways in which these resources are used to solve users’ computing problems.
The operating system controls the hardware and coordinates its use among the various application programs for the various users.
An operating system is similar to a government. it performs no useful function by itself. It simply provides an environment within which other programs can do useful work.
1.1.1 User View
PC: for ease of use, with some attention paid to performance and none paid to resource utilization —how various hardware and software resources are shared.
Mainframe/minicomputer: maximize resource utilization— to assure that all available CPU time, memory, and I/O are used efficiently and that no individual user takes more than her fair share
Workstation/Server: compromise between individual usability and resource utilization.
1.1.2 System View
we can view an operating system as a resource allocator
A control program manages the execution of user programs to prevent errors and improper use of the computer. It is especially concerned with the operation and control of I/O devices.