21,Feb,Tue
Module name: Operating Systems Concepts
Teacher: Xin Huang Email: [email protected] Room: SD461
Assessment
- Final Exam 80%
- Assessment1 10% (Week8)
- Assessment2 10% (Week 14)
Essential Textbook Operating System Concepts 9th
Overview PPT
How a Modern Computer Works
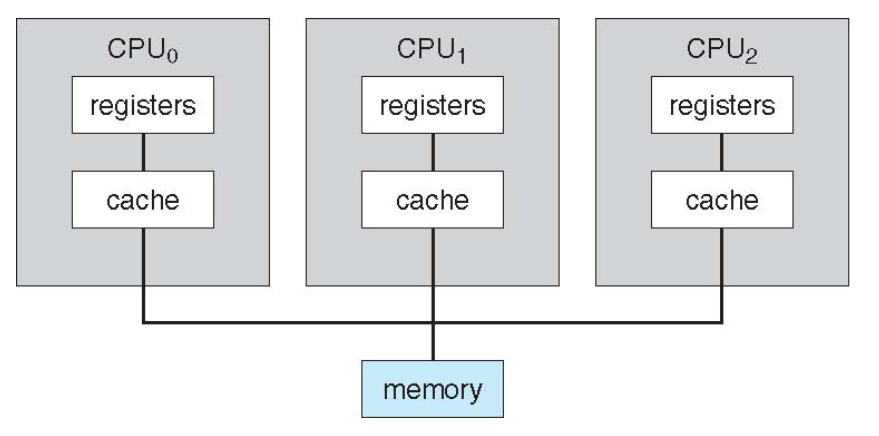
Symmetric Multiprocessing Architecture
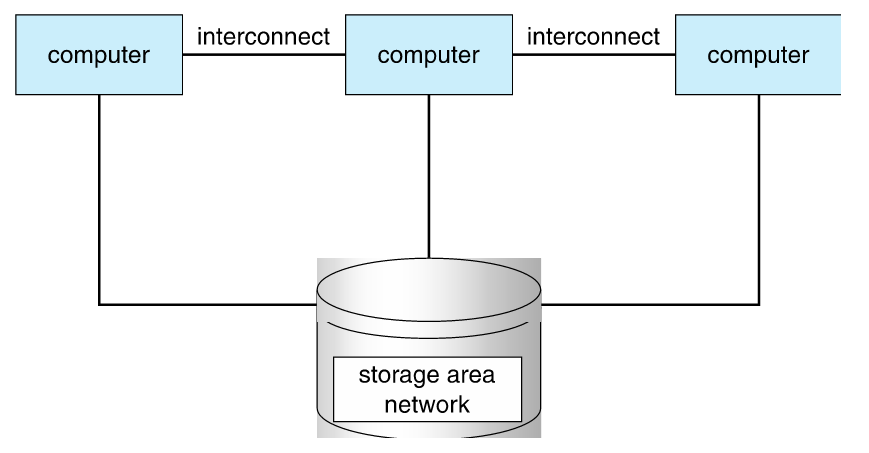
Cluster Systems
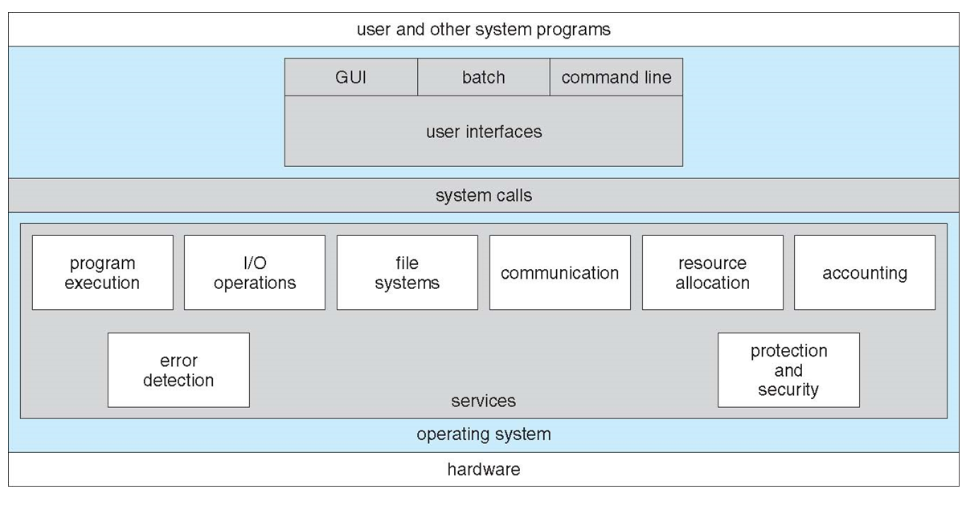
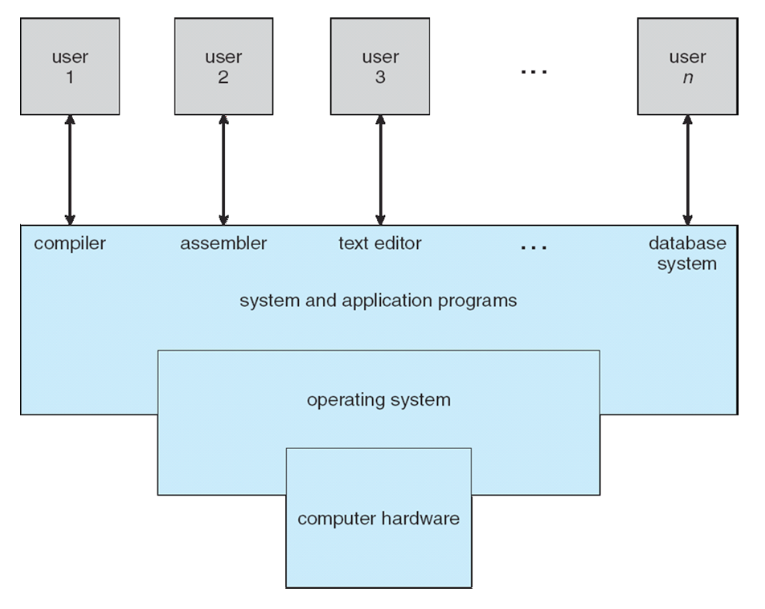
A view of Operating System Services
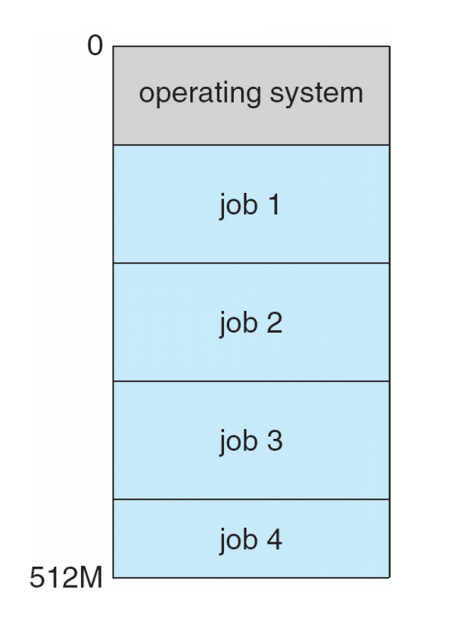
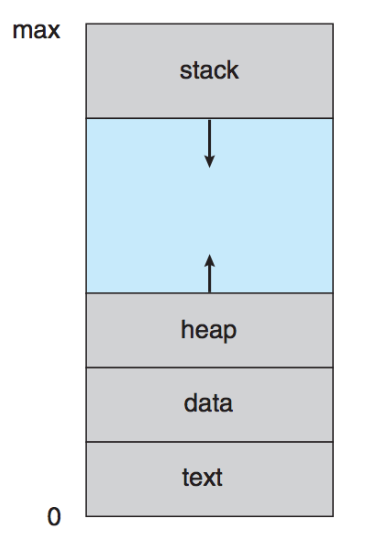
Memory Layout for Multiprogrammed System
pic for MS-DOS
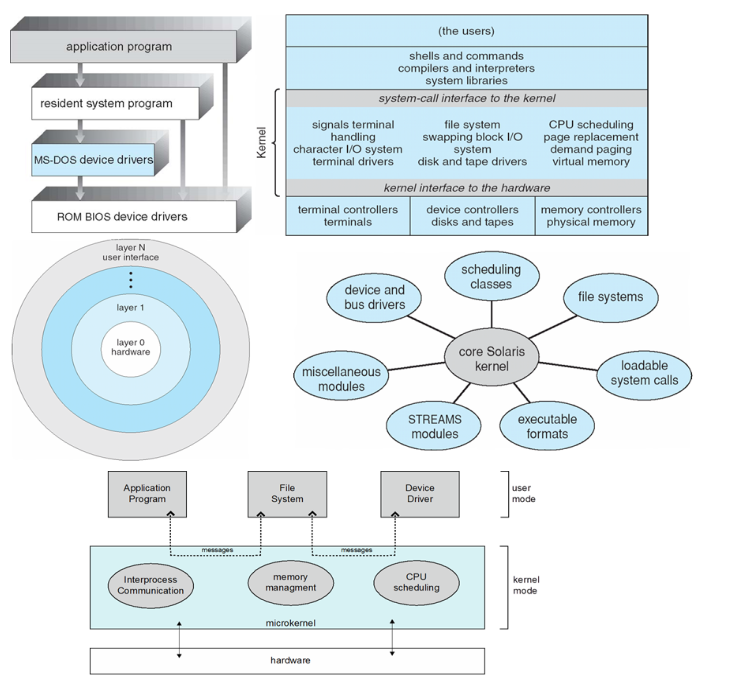
Operating System Structure
- Various ways to Structure on
- Simple structrue- MS-DOS
- More complex -- UNIX
- Layered -- an abstraction
- Solaris Modular Apporach
- Microkernel (funtion limited)
- Hybrid (nowadays use to bulid system)
What Operating Systems Do
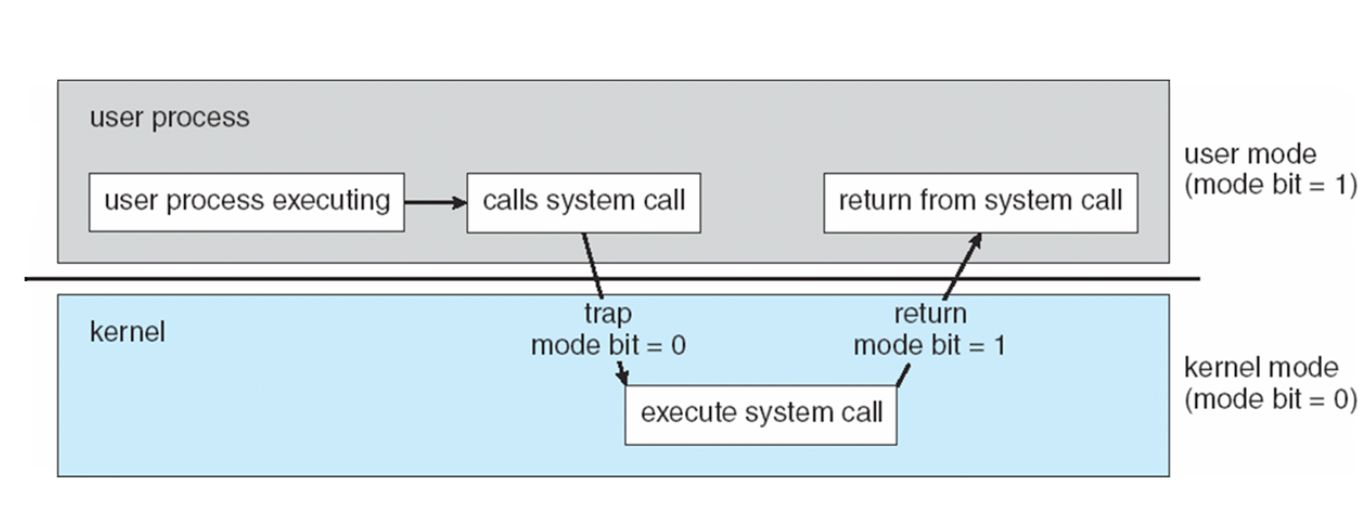
Transition from User to Kernel Mode
API - System Call - OS Relationship
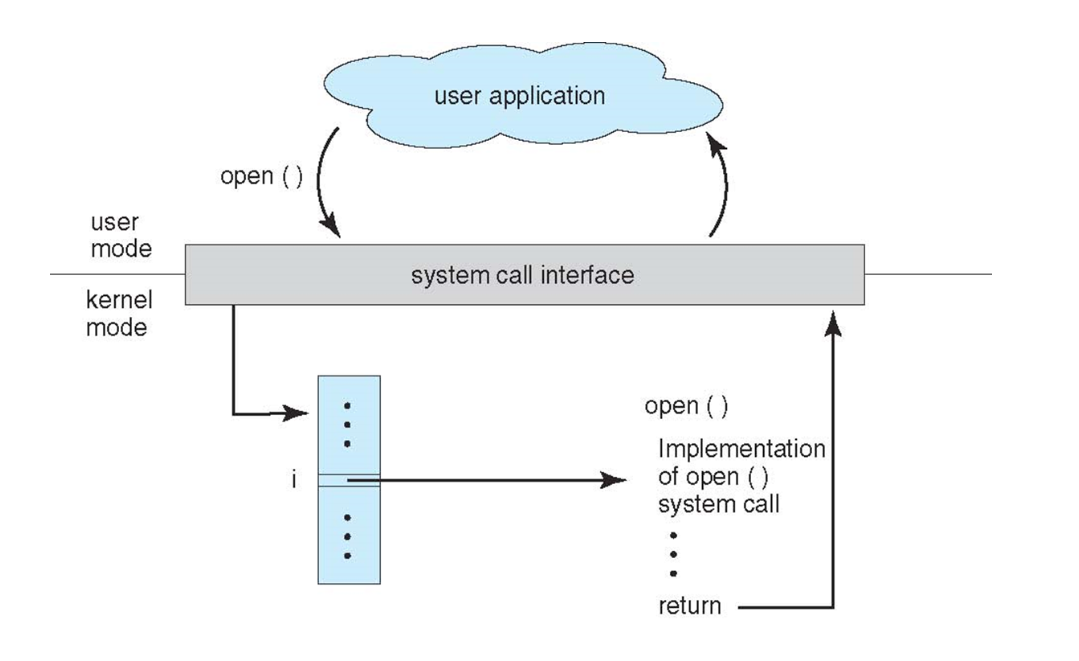
Parameter Passing via Table
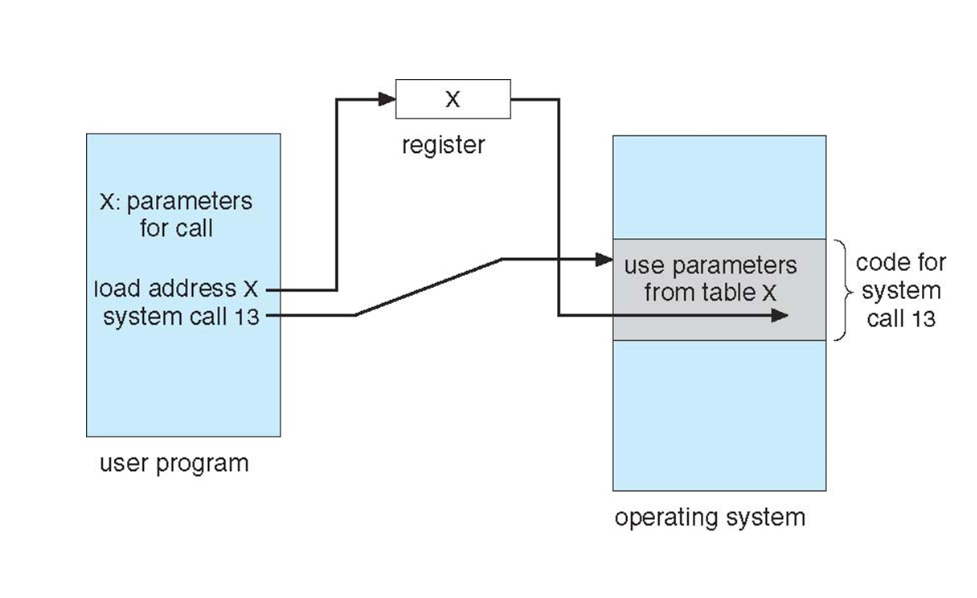
Standard C Library Example
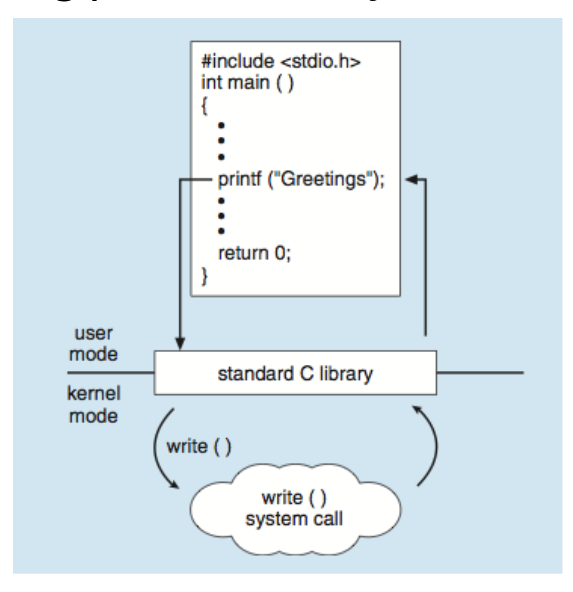
Storage-Device Hierarchy
layer higher, price increase, speed increase, volumn decrease
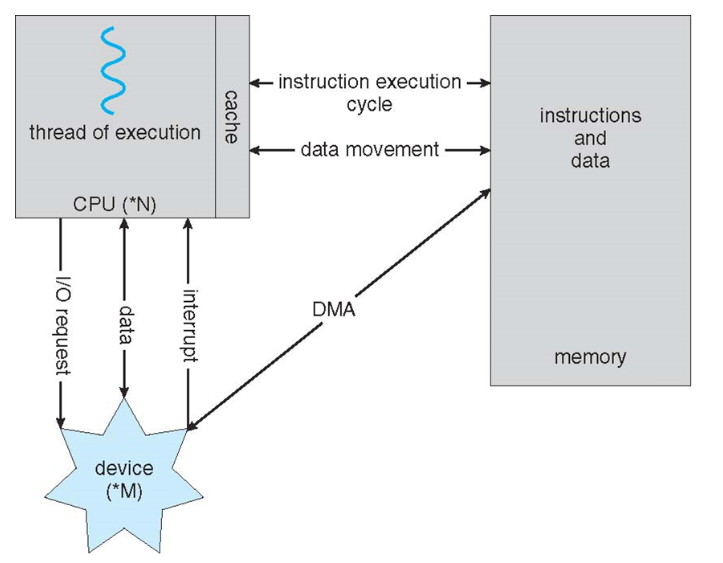
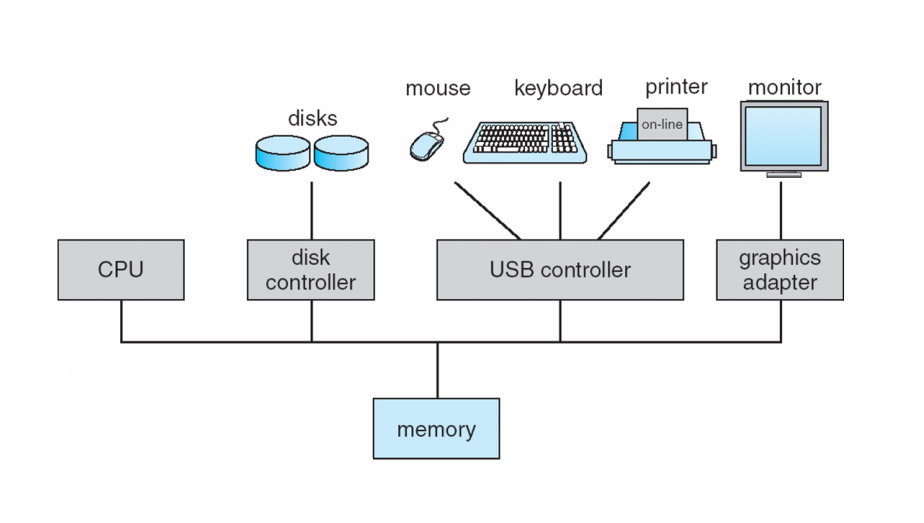
Computer System Organization
Connected using buses
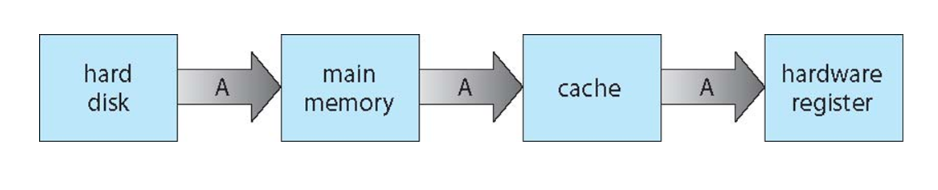
Migration of data "A" from Disk to Register
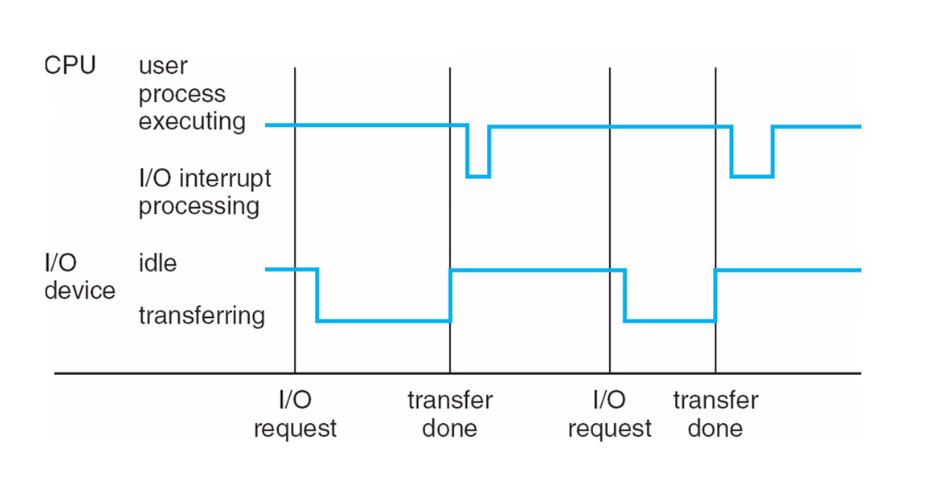
Interrupt
I/O tranfer done, CPU interrupt
Processes PPT
- notation of a Process
- various features of processess
- Scheduling
- Creation
- Termination
- explore interprocess communication
- Shared Memory
- Message Passing
all these charpter are in book
Process Concept
Process
- a program in execution
- process execution must progress in sequential fashion(cpu only handle sequential requeset)
- Process in Memory
Process state
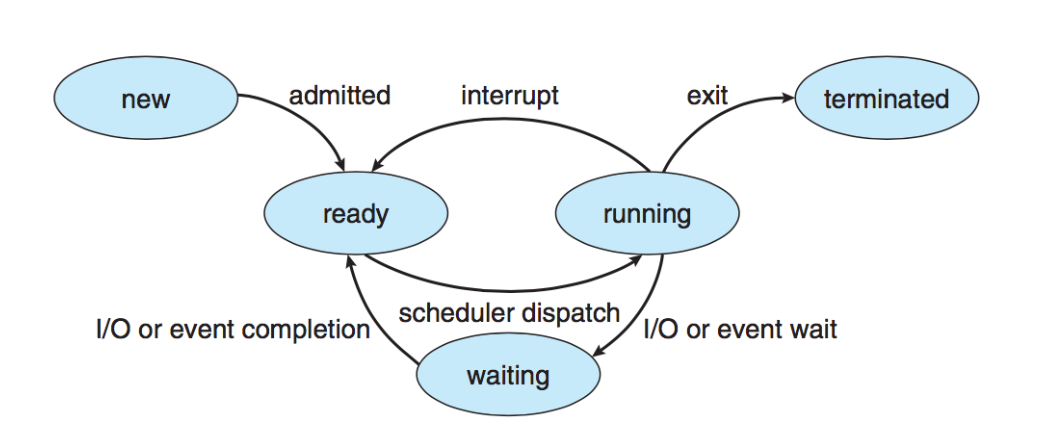
Process Control Block(PCB)

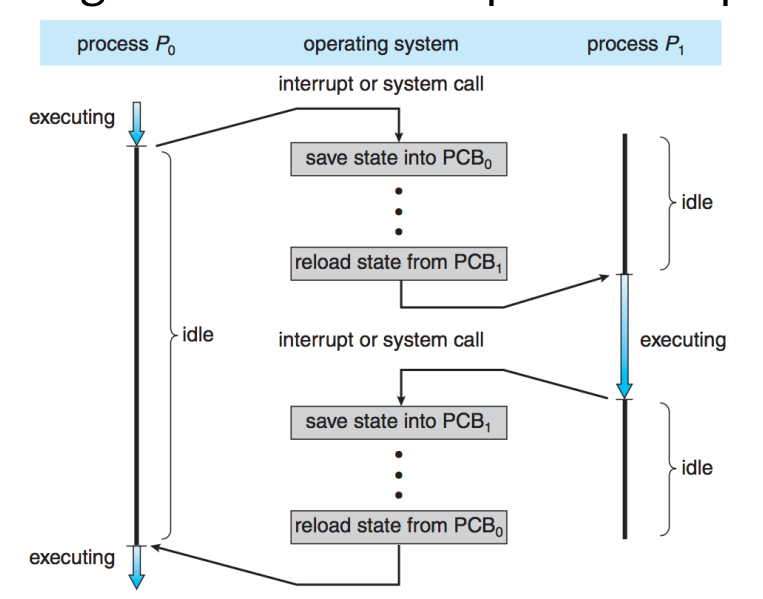
- Diagram showing CPU switch from process to Processes
Process Scheduling
Process scheduler
- Selects among available processes for next execution on CPU
- Maintains scheduling queues of Processes
- Job queue - set of all processes in the System
- Ready queue - set of all processes residing in main memory, ready and waiting to execute
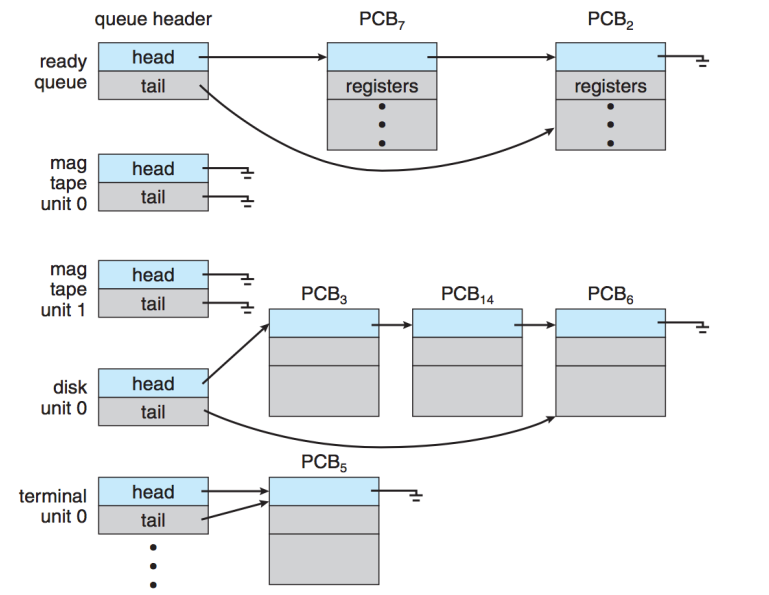
- Device queues - set of processes waiting for an I/O device
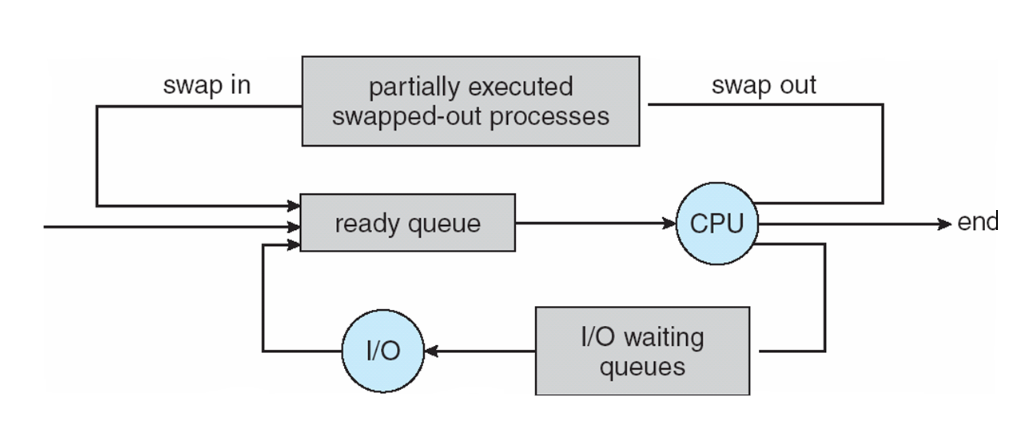
The ready queue and various I/O device queues
- Queueing-diagram representation of process Scheduling
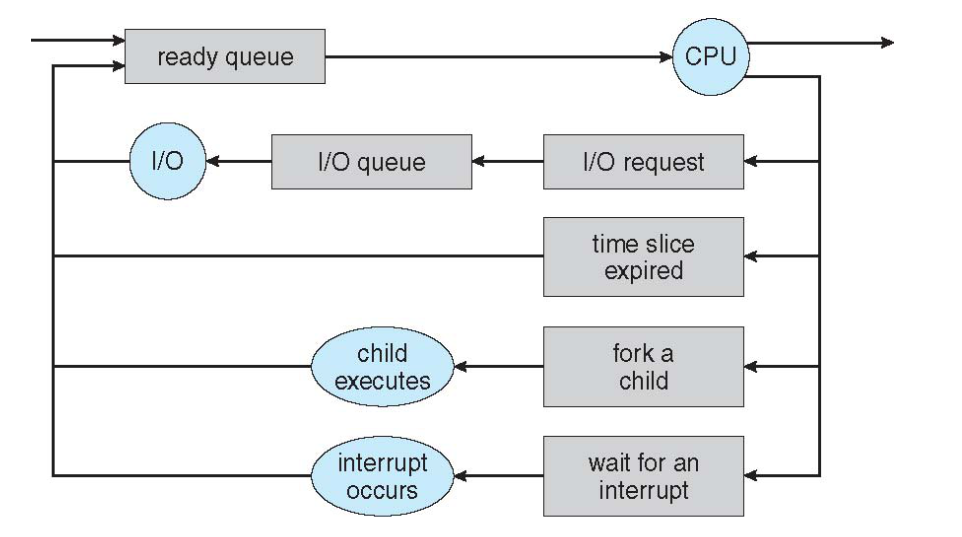
- Short-term scheduler (or CPU scheduler) - selects which porcess should be executed next and allocates CPU
- Long-term scheduler (or job scheduler) - selects which processes should be brought into the ready queue
- I/O-bound process - spends more time doing I/O than computations, many short CPU bursts
CPU-bound process - spends more time doing computations; few very long CPU bursts
Addition of medium-term scheduling to the queueing diagram
- Context switch
- When CPU switches to another process, the system must save the state of the old process and load the saved state for the new process via a context switch
- Context of a process represented in the PCB
Operations on Process
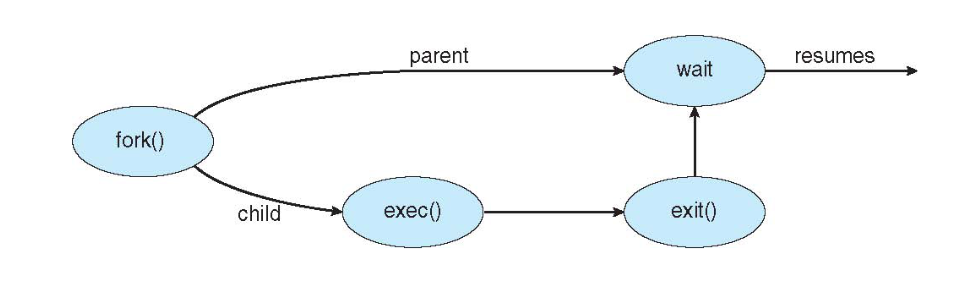
Process Creation
- Parent process Creatione children processes, which, in turn create other processes, forming a tree of processes
- C Program Forking Separate Processes

Process Termination
Process executes last statement and then asks the operating system to delete it using the exit() system call.
- Returns status data from child to parent (via wait())
- Process' resources are deallocated by operating system
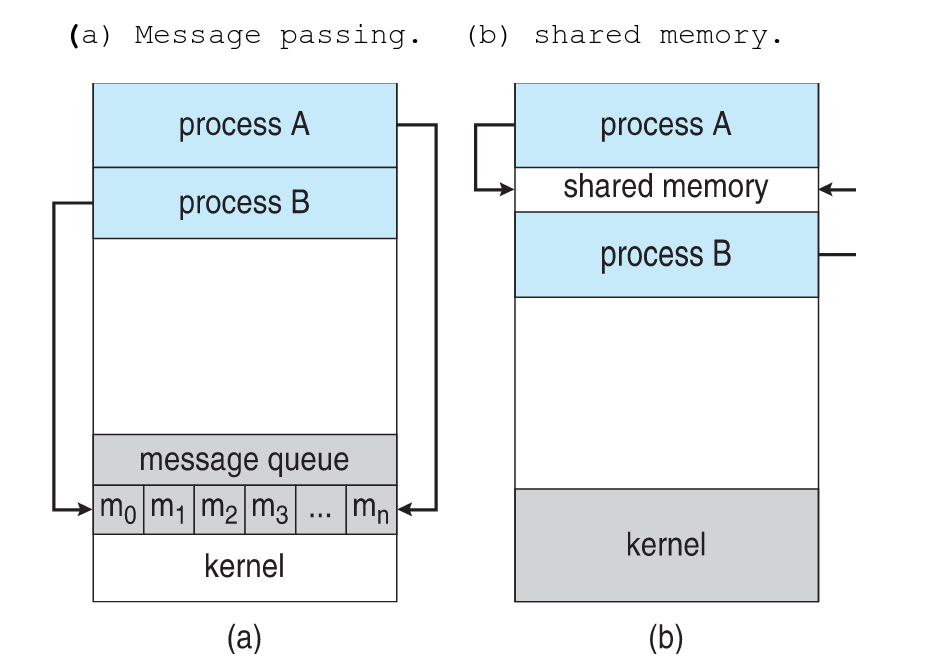
Interprocess Communication Communications Models
Producer-Consumer Problem
- Paradigm for cooperating processes, producer process produces information that is consumed by a consumer process
Bounded-Buffer - Shared -Memory Solution

Bounded-Buffer -Producer

Bounde-Buffer -Consumer

Interprocess Communication - Message Passing
- IPC facility provides two opertions:
- send(message)
- receive(message)
Direct Communication
- Processes much name each other explicitly:
- send(P,message) - send a message to process P
- recevie(Q,message) - receive a message from process Q
Indirect Communication
- create a new mailbox (port)
- send and receive messages through mailbox
- send(A, message) - send a message to mailbox A
- receive(A, message) - receive a message from mailbox A
- destroy a mailbox
Synchronization

Threads PPT
Objectives
- notion of a Threads
- APIs
Threads
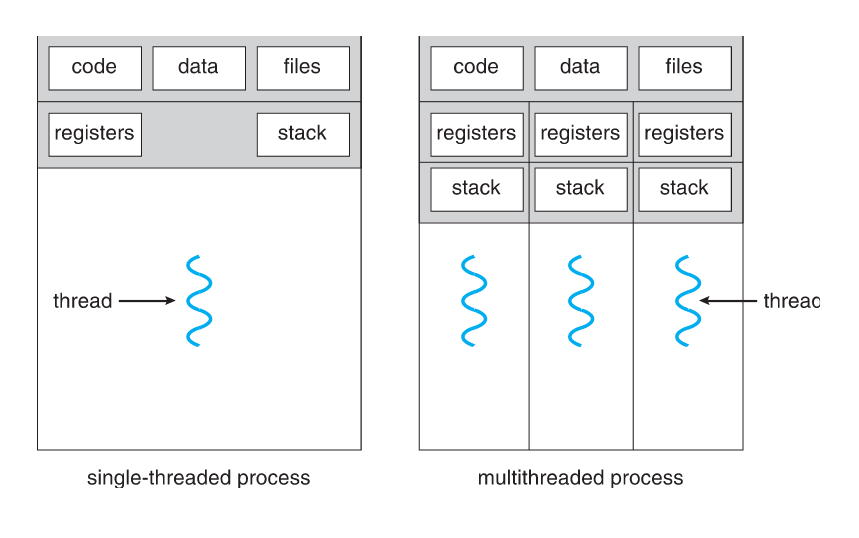
- Thread -- a fundamental unit of CPU utilization that forms the basis of multithreaded computer Systems
Single and Multithreaded Processes
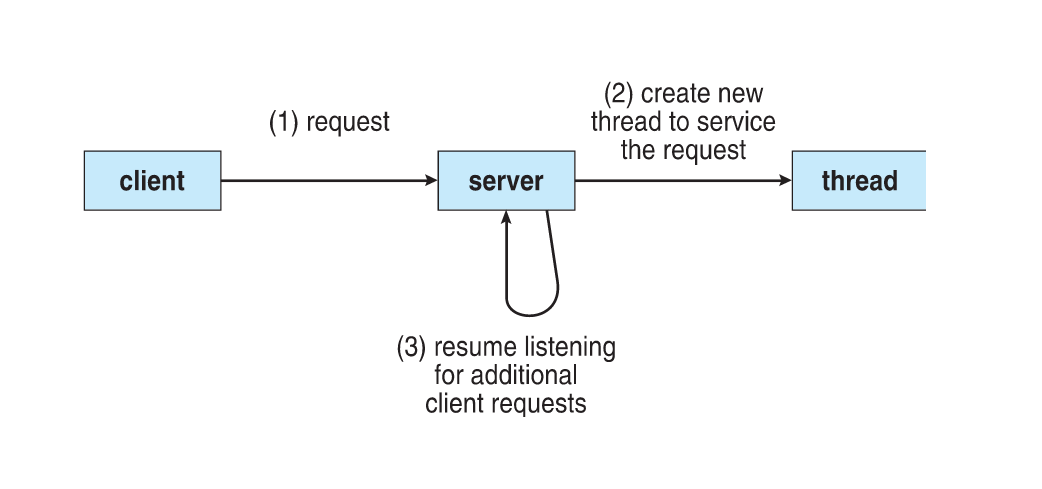
Multithreaded Server Architecture
Benefits
- Resopnsiveness - many allow continued execution if part of process is blocked, especially important for user inter faces
- Resource Sharing - threads share resources of process, easier than shared memory or message Passing
- Economy - cheaper than process creation, thread switching lower overhead than context switching
- Scalability - process can take advantage of multiprocessor architectures
Multithreading Models User Threads and Kernel Threads
- User threads - management done by user-level threads library
- Kernel threads - Supported by the Kernel
many-to-One
- Many user-level threads mapped to single kernel Thread
- One thread blocking causes all to block
- Multiple threads may not run in parallel on muticore system because only one may be in kernel at a time
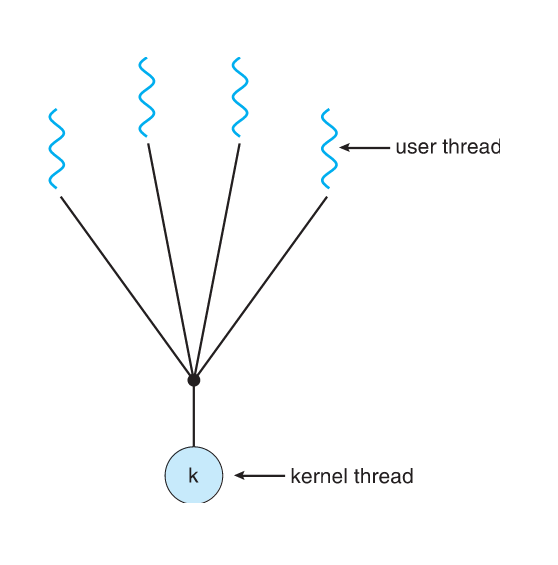
One-to-One
- Each user-level thread maps to kernel Thread
- More concurrency than many-to-one
- Number of threads per process sometimes restricted due to overhead
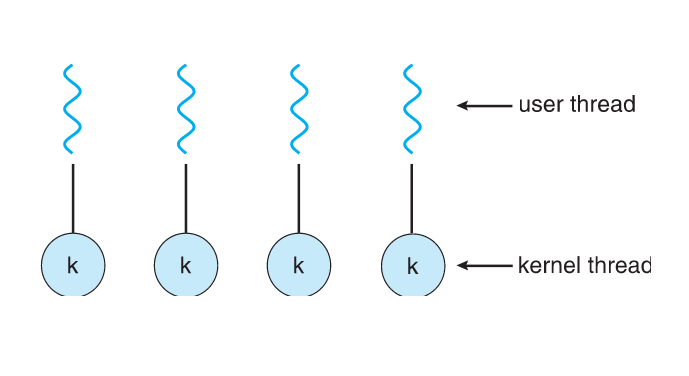
Many-to-Many
- Allows many user level threads to be mapped to many kernel threads
- Allows the operating system to create a sufficient number of kernel threads
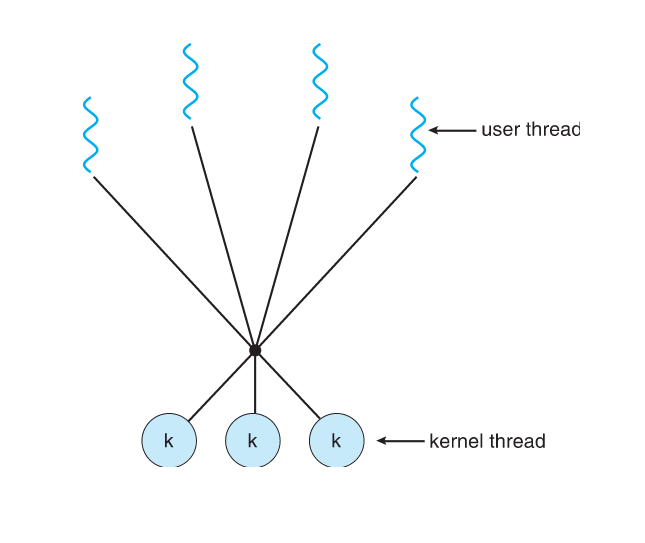
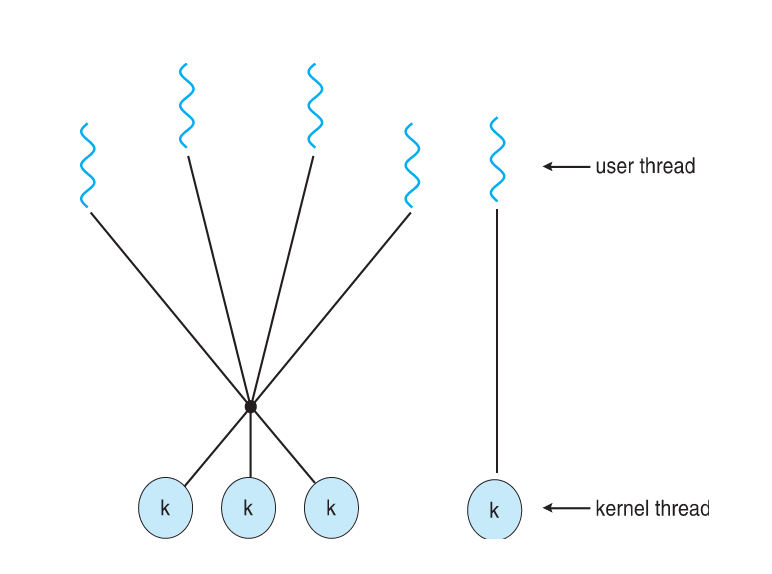
Two-level Model
- Similar to M:M, except that it allows a user thread to be bound to kernel thread
Thread Libraries
- Thread library provides programmer with API for creating and managing threads Pthreads
- May be provided either as user-level or kernel-level
- API specifies behavior of the thread library, implementation is up to development of the Library
- Common in UNIX operating Systems
Pthreads Code for Joining 10 Threads

Implict Threading
- Growing in populrity as numbers of threads increase, program correctness more difficult with explicit threads
- Creation and management of threads done by compilers and run-tim libraries rather than programmers
Q&A
- What are the three main purposes of an operating system?
- Provide an environment for a computer user to execute programs on computer hardware in a convenient and efficient manner
- To allocate the separate resources of the computer as needed to solve the problem given. The allocation process should be as fair and efficient as possible
- As a control program it serves two major functions:
- Supervision of the execution of user programs to prevent errors and improper use of the computer
- Management of the operation and control of I/O devices
What is the purpose of system calls?
System call allow user-level processes to request services of the operating system
Including the initial parentprocess,how many processesarecreated by the program?

8
Provide two programming examplesin which multithreadingprovides better performance than a single-threaded solution.
a. A web server that services each request in a separate thread b. A parallelized application such as matrix multiplication where different parts of the matrix may be work on in parallel c. An interactive GUI program such as a debugger where a thread is used to monitor user input, another thread represents the running application.